EvacuAIDi: An AI-Driven, Causal-Informed Framework for Probabilistic and Disability-Inclusive Evacuation Guidance
A comprehensive AI-driven framework to revolutionize building evacuations through standards-compliant automation, disability-inclusive modeling, causal evaluation, and probabilistic risk assessment.
PhD Dissertation 2025
Amir Rafe • Utah State University
Conducted under the supervision of Dr. Patrick Singleton
Research Overview
This dissertation addresses critical gaps in evacuation science through four interconnected research contributions that form the comprehensive EvacuAIDi framework.
The Critical Research Gaps
Standards-Compliant Evacuation Simulation Inputs Generation
Most existing simulation workflows rely on manual extraction of parameters from fire safety codes (e.g., NFPA 101, SFPE), which is error-prone and lacks causal traceability. This creates inconsistencies across studies and weakens the credibility of simulation results.
Gap: There is no widely adopted, automated pipeline to extract, reason over, and validate evacuation input parameters in a way that guarantees both standards compliance and causal coherence.
Disability-Inclusive Behavioral Fidelity
While many evacuation models include agents with reduced mobility or altered walking speeds, few go beyond kinematic simplifications. Key behavioral aspects, such as leadership dynamics, marshal guidance, and probabilistic compliance, are poorly captured for individuals with disabilities.
Gap: There is a critical need for empirically calibrated models that realistically simulate both the physical constraints and behavioral responses of heterogeneous groups, including disabled individuals.
Causal and Probabilistic Evaluation of AI Guidance
Studies that consider AI guidance during evacuation frequently rely on deterministic assumptions and average-case analyses, failing to account for uncertainty in key behavioral factors such as occupant compliance, as well as contextual variables like occupant load.
Gap: A robust, scenario-aware framework for evaluating the causal and probabilistic impact of AI guidance on evacuation safety under uncertainty remains underdeveloped.
Central Research Questions
RQ1: Automated Simulation Parameters Extraction
How can AI be leveraged to automate the extraction of simulation parameters from complex regulatory documents to ensure that models are both standardscompliant and causally coherent?
RQ2: Disability-Inclusive Behavioral Modeling
How can agent-based models be enhanced to realistically simulate the evacuation dynamics of a heterogeneous crowd, including individuals with disabilities, by incorporating empirically-derived social and behavioral forces?
RQ3: Causal Impact of AI Guidance Compliance
What is the quantifiable causal effect of occupant compliance with a personalized, accessibility-aware AI guidance system on evacuation performance across a range of hazard scenarios?
RQ4: Probabilistic Risk Assessment Framework
How can a probabilistic framework be used to formally integrate uncertainty in human compliance and occupant load to produce a robust assessment of evacuation risk?
Research Architecture
Introduction & Problem Formulation
Established the critical need for AI-driven, disability-inclusive evacuation systems by identifying major gaps in current evacuation modeling approaches and defining the four primary research questions.
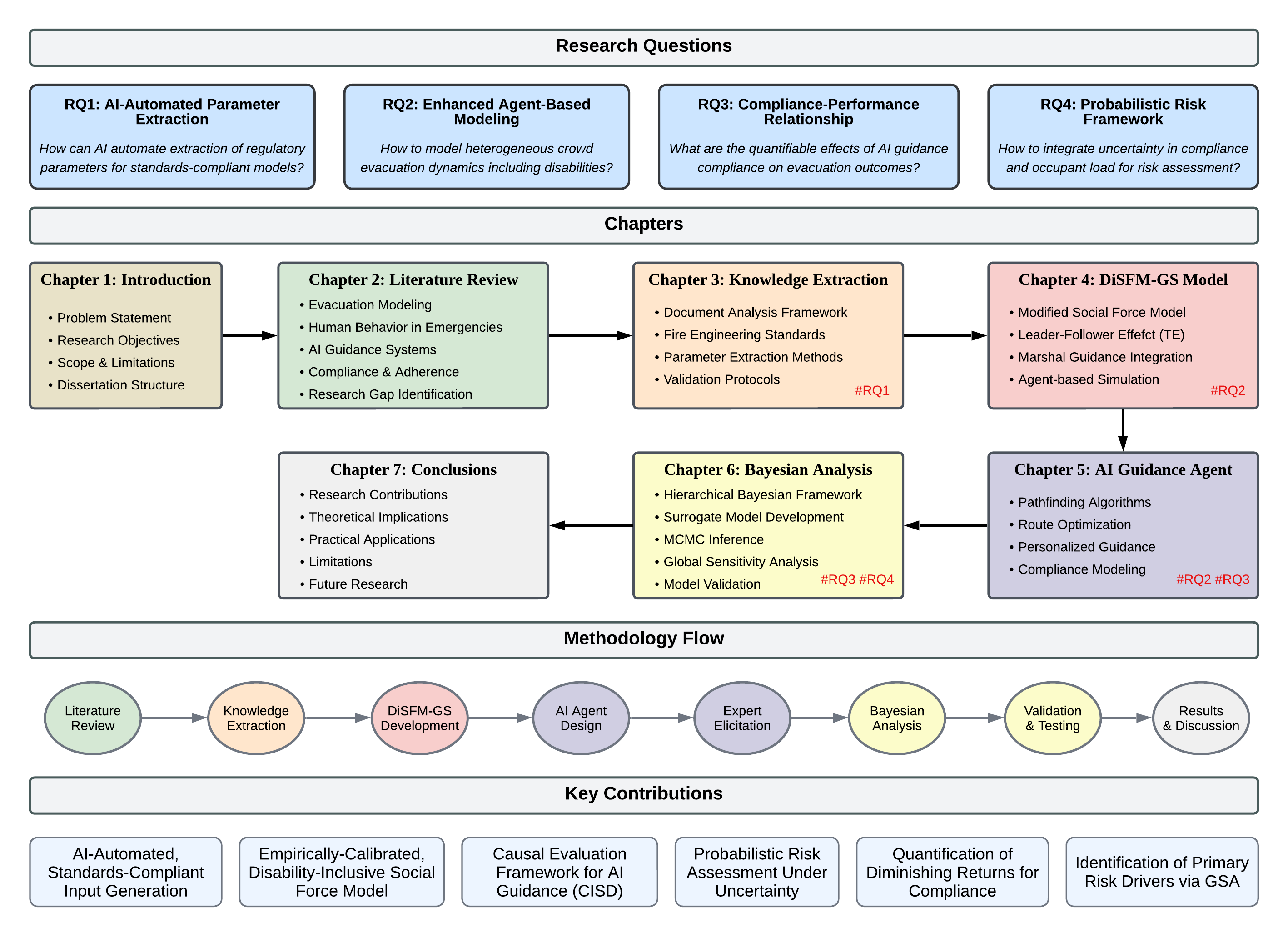
Research Framework Structure
Literature Review: Who Leads, Who Follows?
Systematic review of 233 peer-reviewed studies on evacuation guidance and leader-follower dynamics, covering human-led, environmental, technological, and hybrid guidance systems to establish the theoretical foundation.
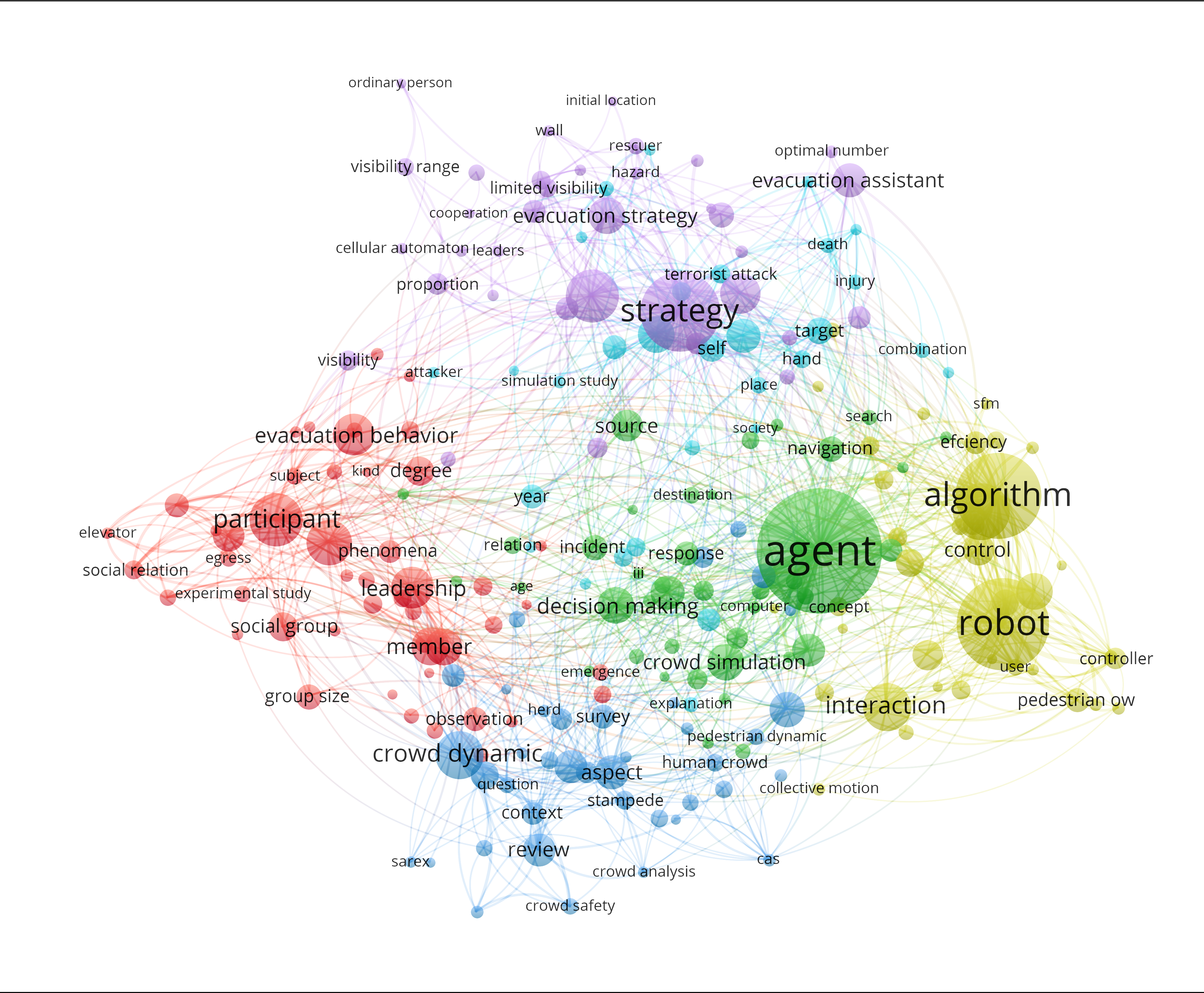
Literature Classification Framework
Causal AI for Evacuation Modeling
Developed an AI pipeline that automatically parses regulatory documents (NFPA 101, SFPE Handbook, BS-9999, etc.) using fine-tuned LLM, GraphRAG, and causal reasoning to generate simulation-ready parameters with 92%+ accuracy.
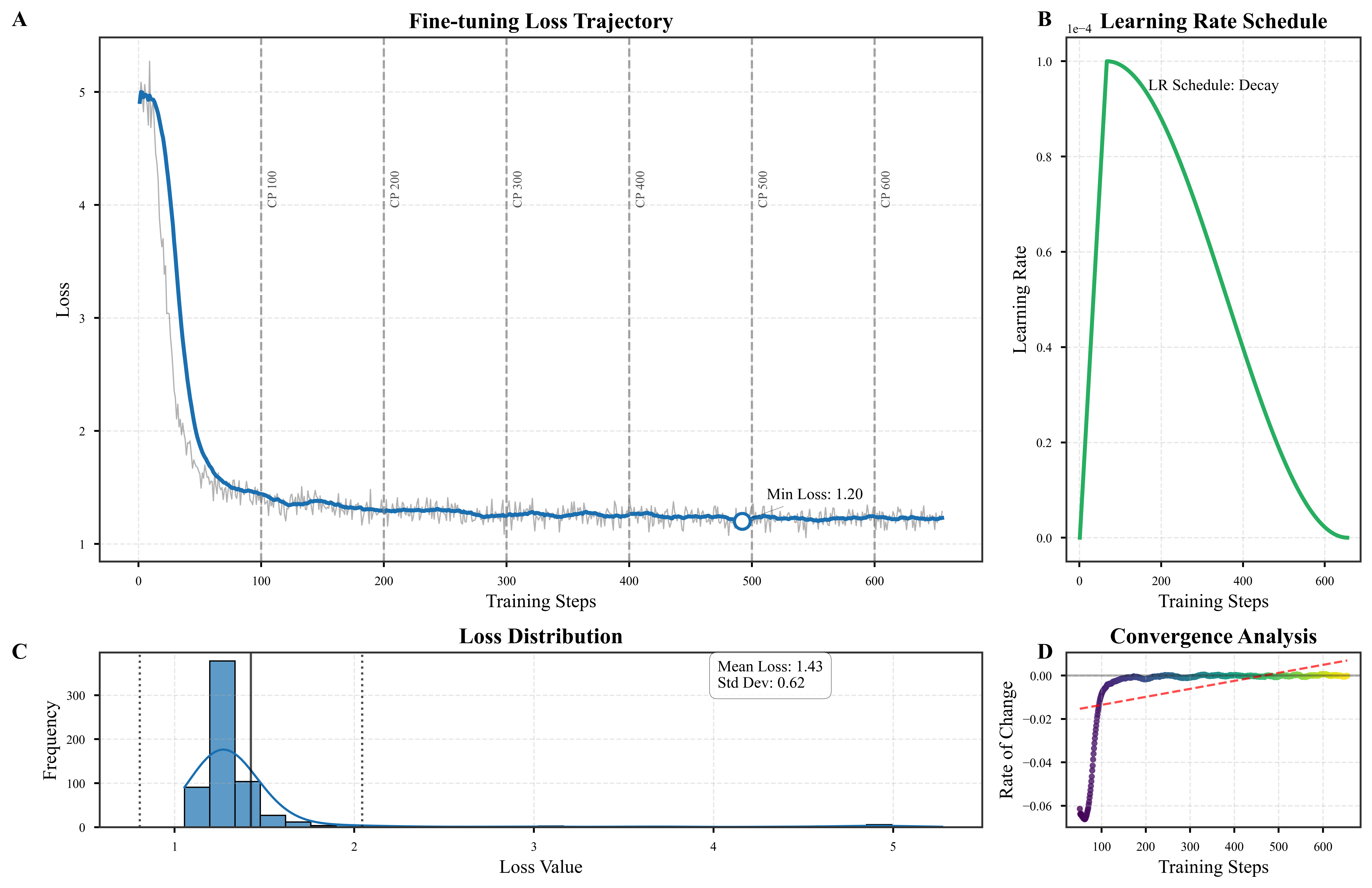
Training dynamics of the fine-tuned Gemma 3 (4B) model
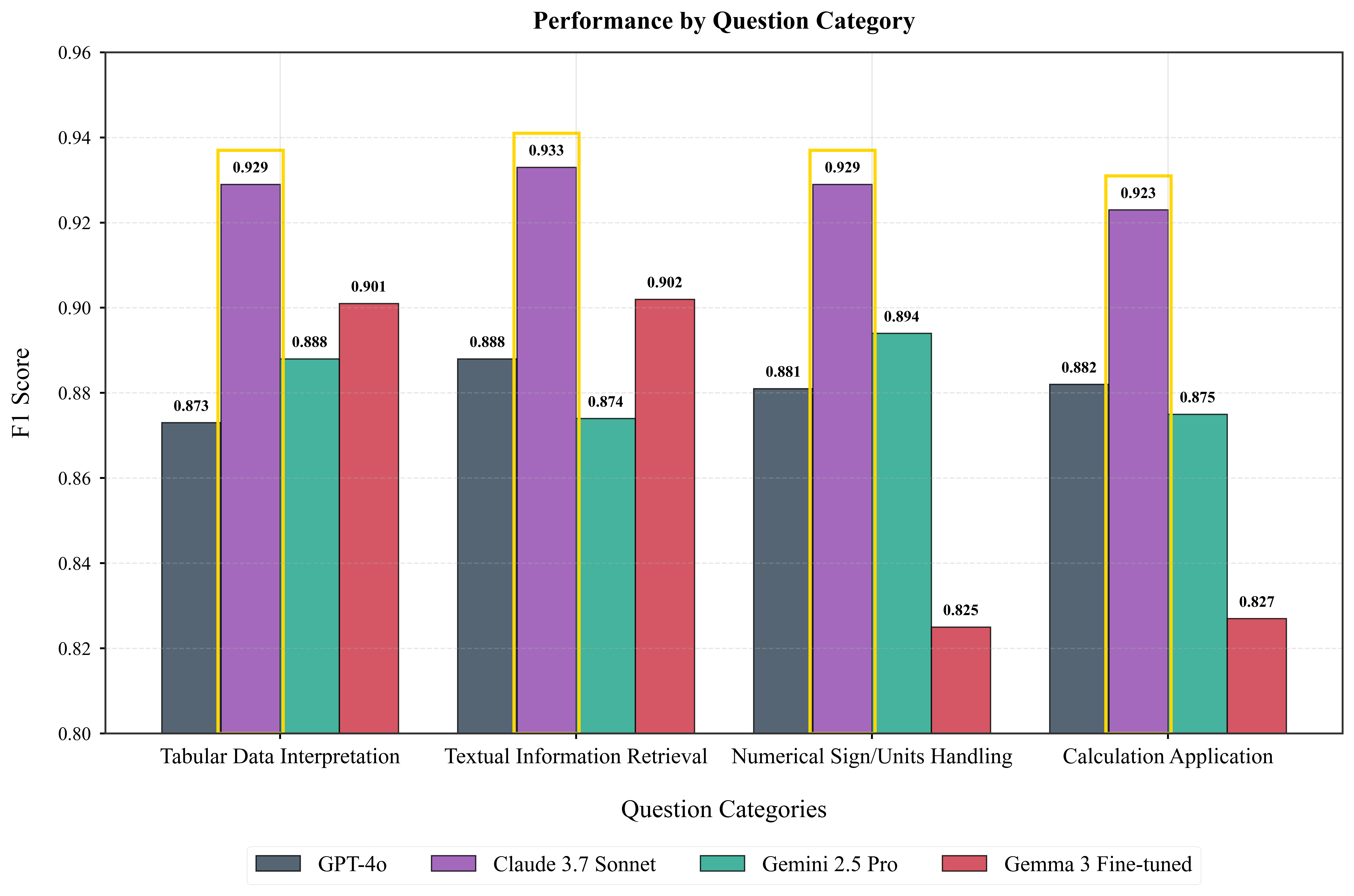
Performance of four LLMs across evacuation-related question categories
Disability-Inclusive Social Force Model (DiSFM-GS)
Enhanced agent-based modeling by incorporating empirically-calibrated parameters for individuals with disabilities, using RFID trajectory data from controlled evacuation drills in a 4-story university building.
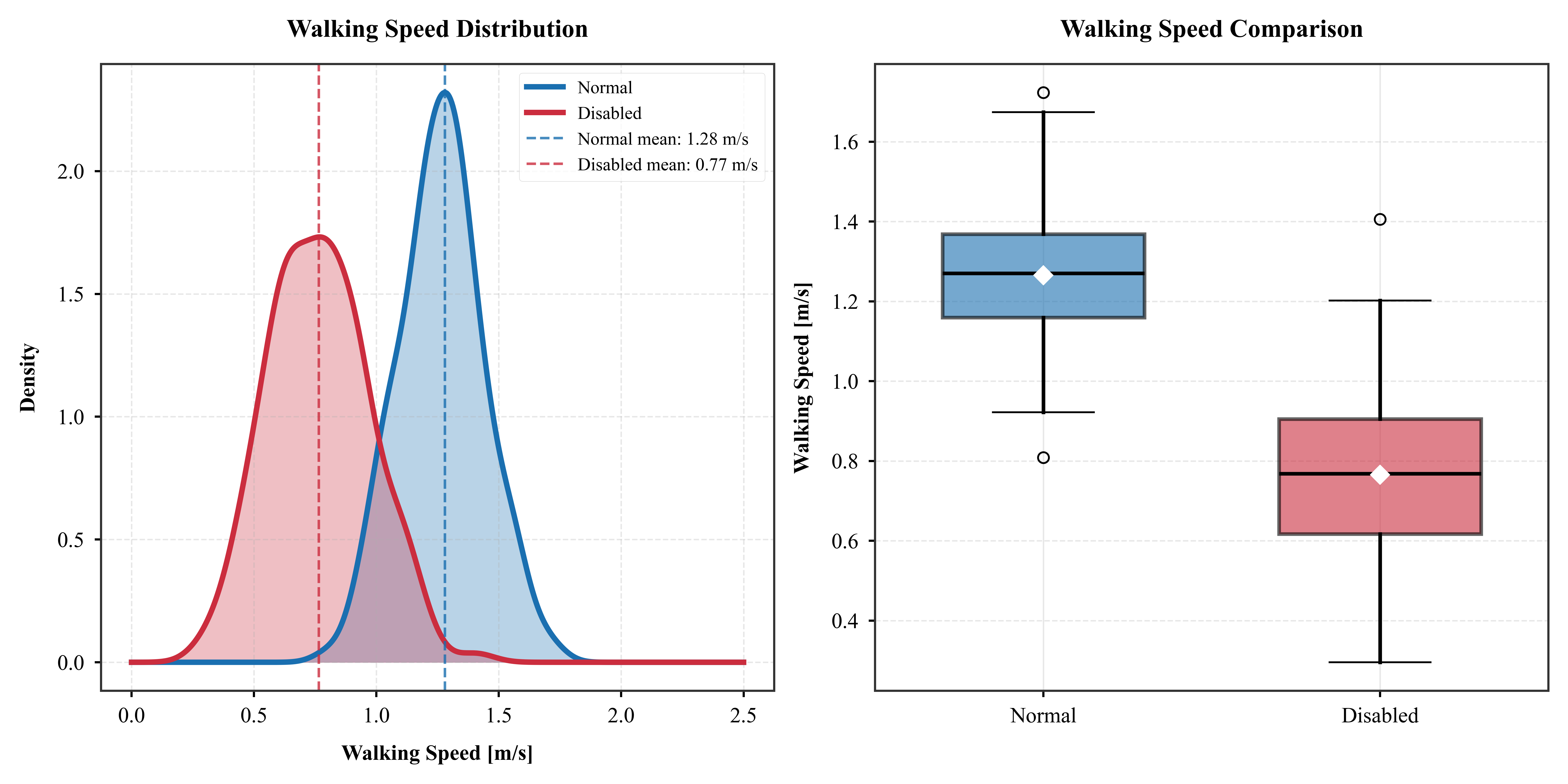
Walking Speed Analysis
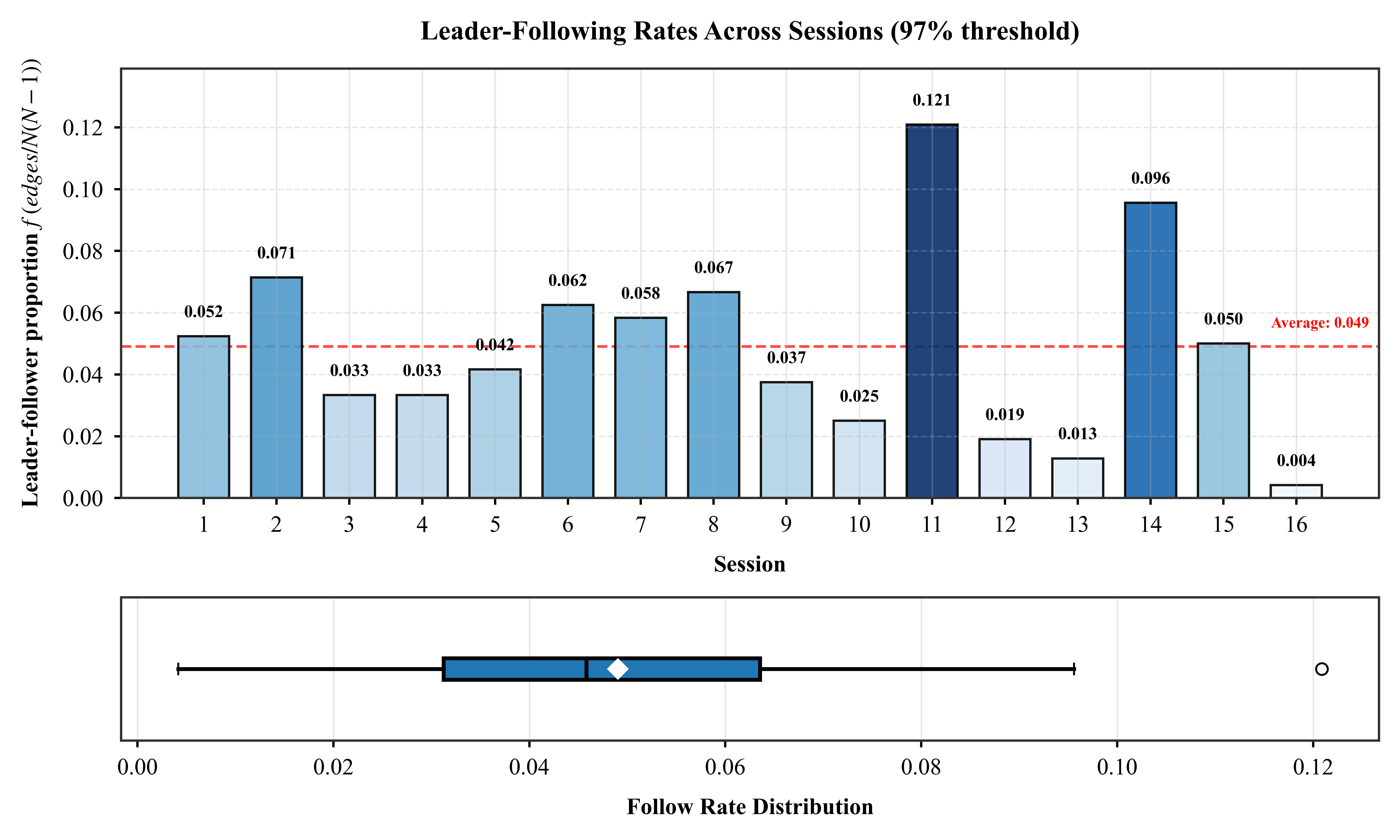
Leader-following rates
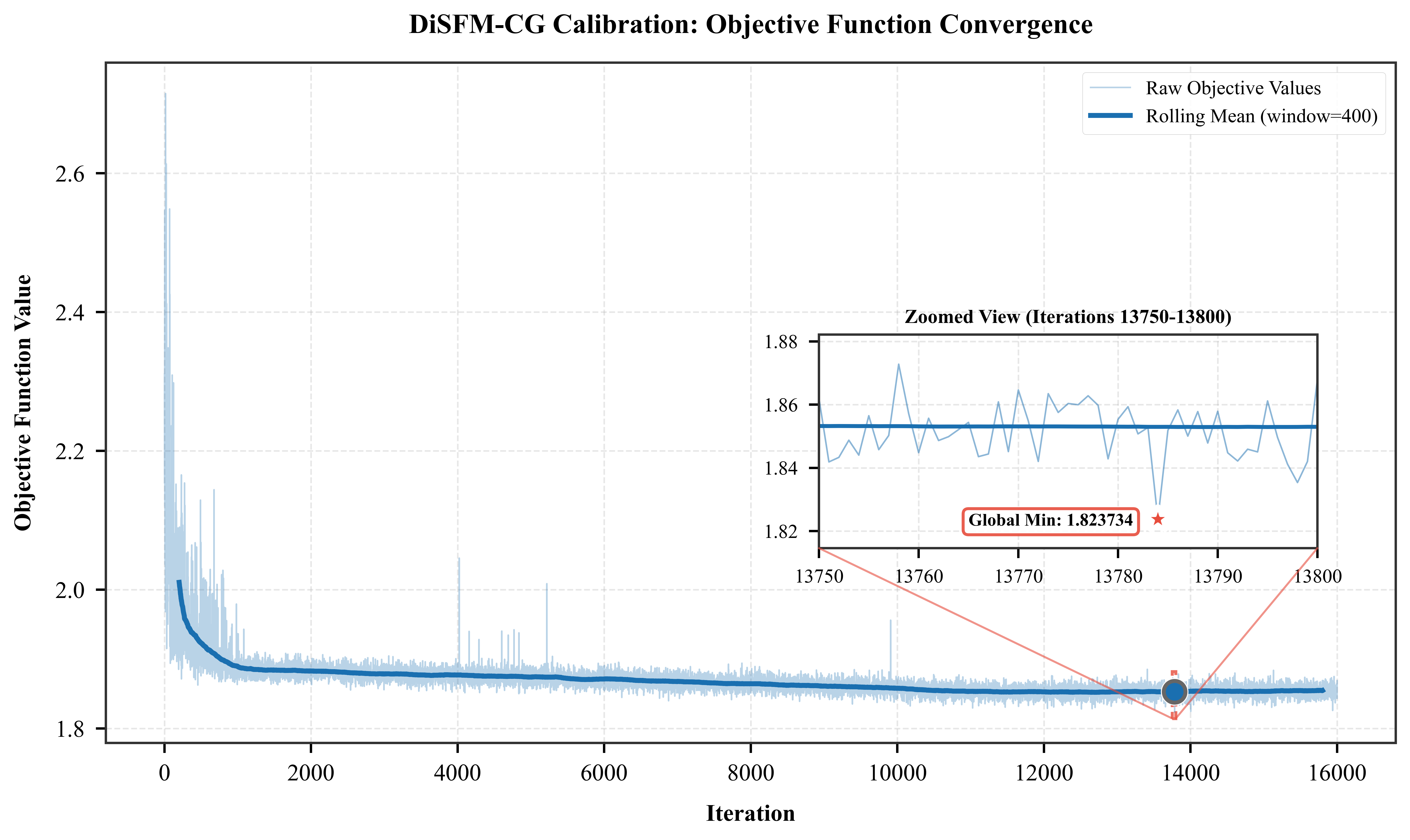
Objective function convergence
Causal-Intervention Scenario Design (CISD)
Used counterfactual simulations and Pearl's do-calculus to isolate the causal impact of AI guidance compliance on evacuation performance, demonstrating a 22.5% reduction in evacuation time across diverse scenarios.
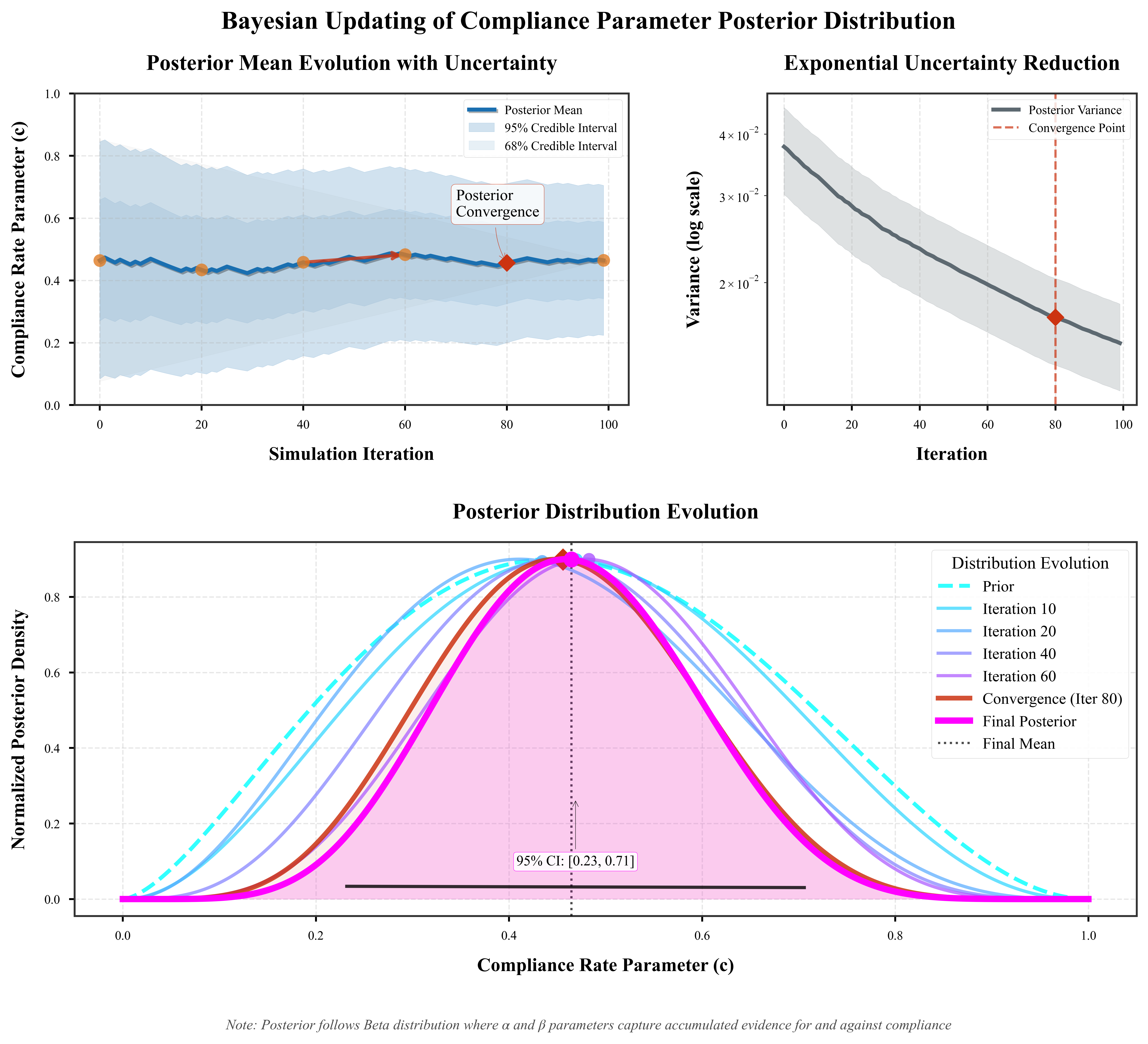
Posterior Evolution
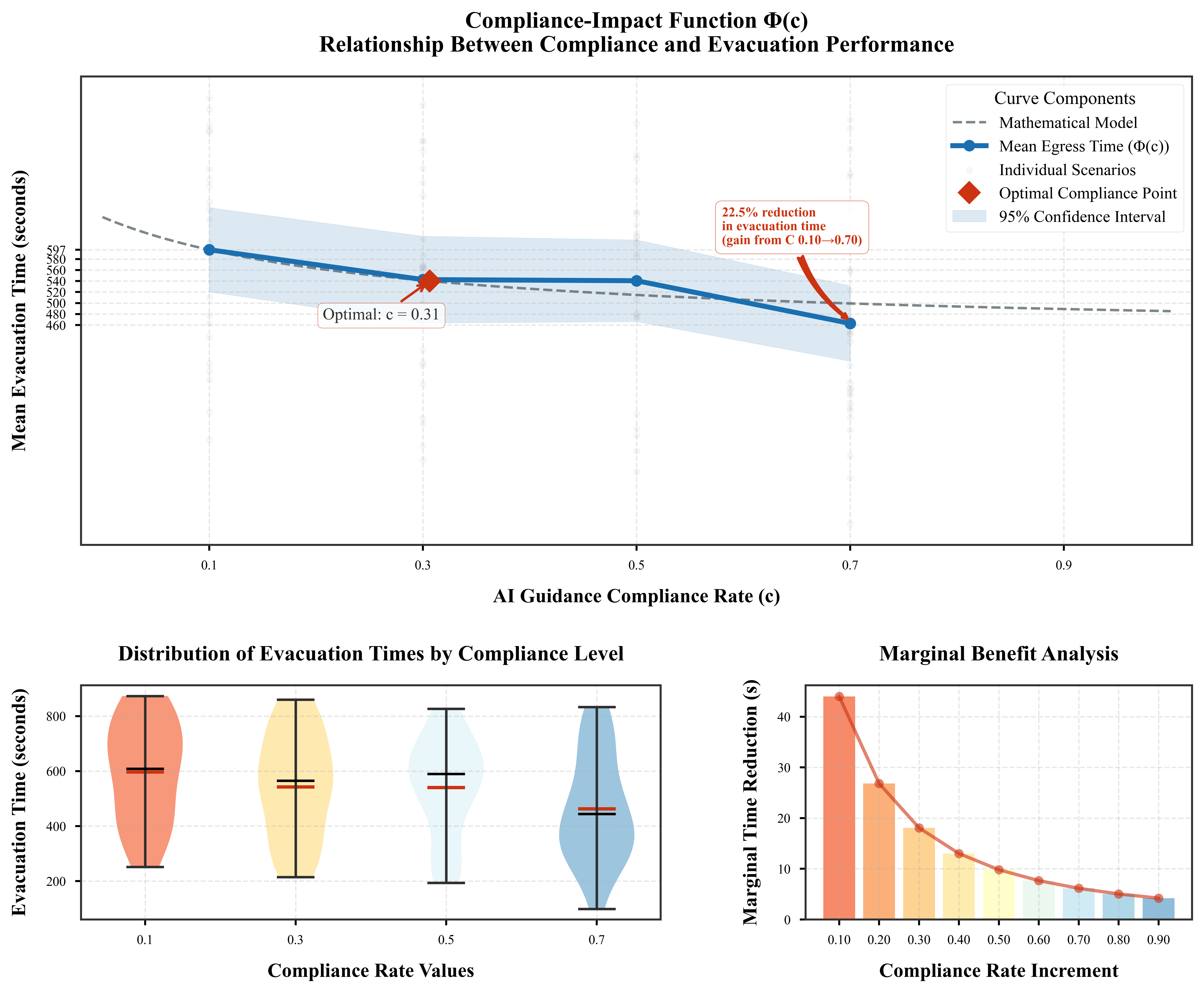
Compliance Impact Analysis
Hierarchical Bayesian Risk Framework
Developed probabilistic risk assessment integrating uncertainty in compliance and occupant load using Gaussian Process surrogates and Global Sensitivity Analysis, identifying occupant load as the primary risk driver (57% of variance).
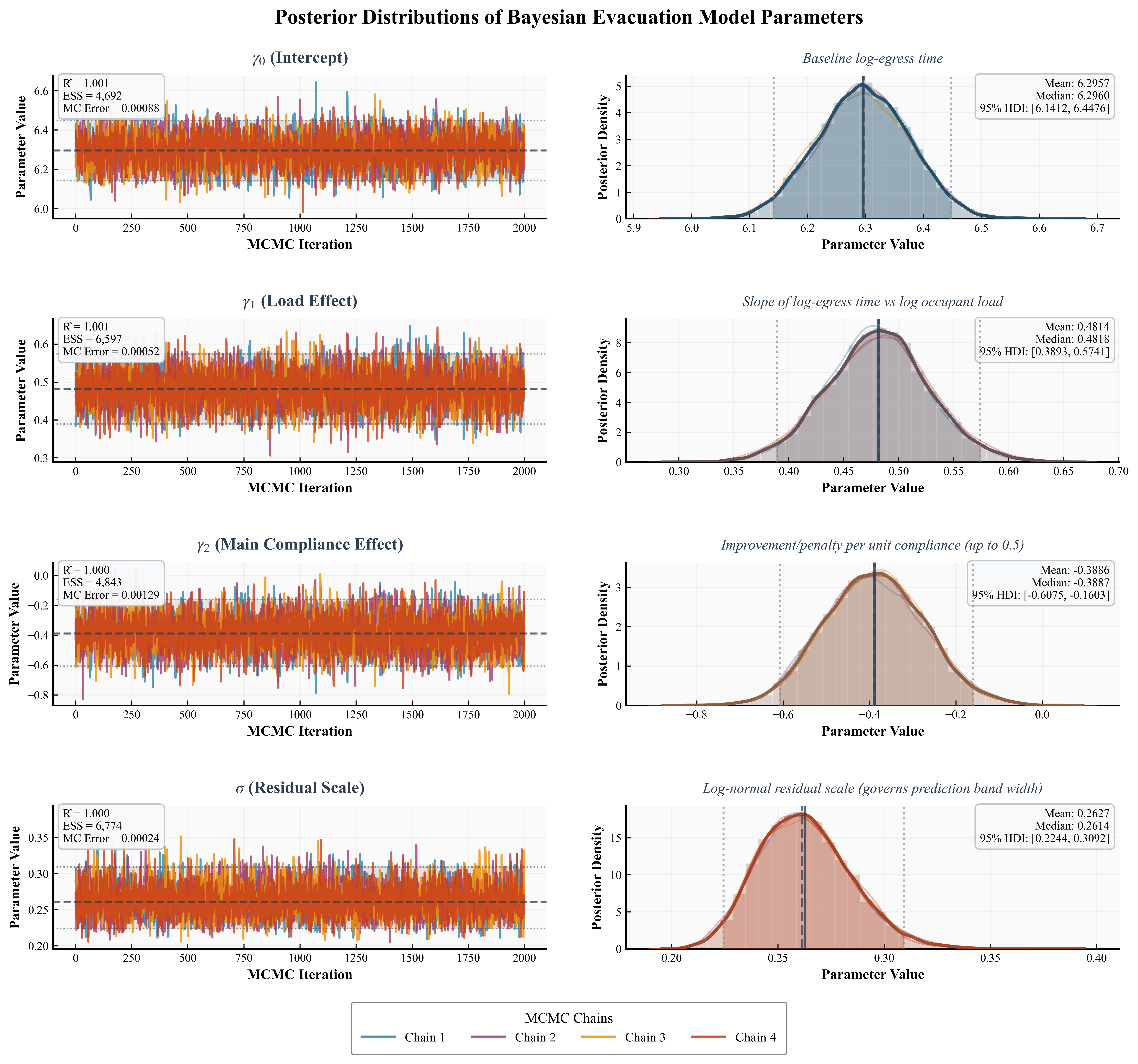
MCMC Trace Plots
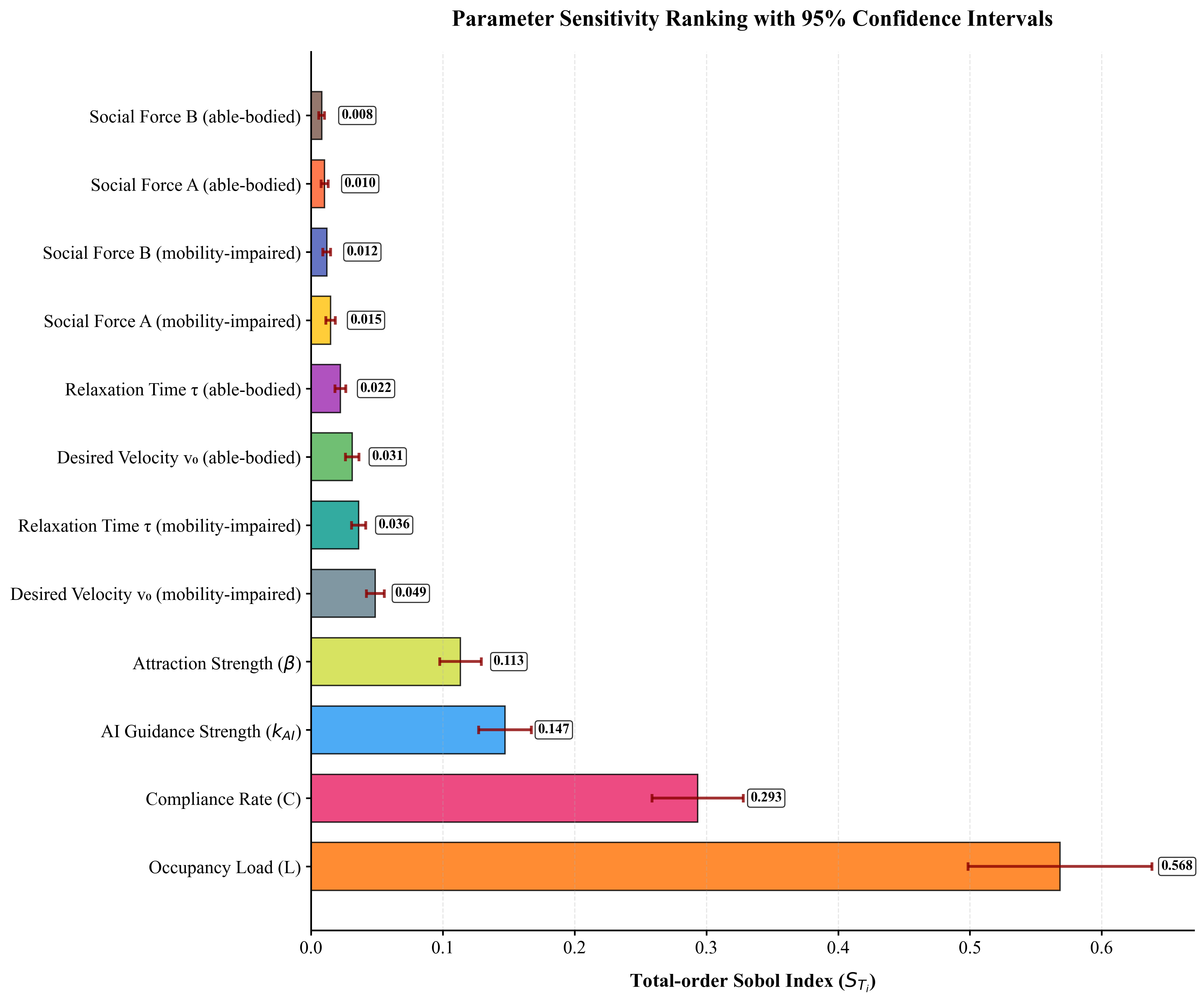
Parameter Sensitivity Ranking
Conclusions & Future Directions
Synthesized research contributions, quantified stakeholder implications, and outlined future research directions including integration with CFD models, multimodal guidance systems, and dynamic trust modeling.
Key Research Findings
Empirical results demonstrating the effectiveness and impact of the EvacuAIDi framework across multiple dimensions.
🎯 Causal Impact of AI Guidance
Reduction in mean evacuation time
Increasing AI compliance from 10% to 70% causes a statistically significant 22.5% reduction in evacuation time, with diminishing returns beyond 50% compliance.
♿ Equity Enhancement
Stronger benefit for vulnerable populations
AI guidance provides 15.9% greater benefits for individuals with disabilities, actively helping to close the safety gap and promote equity.
📊 Primary Risk Drivers
Global Sensitivity Analysis identifies these two factors as primary drivers of evacuation risk variance.
🤖 LLM Performance
Parameter extraction accuracy
The RAG pipeline achieves over 92% accuracy in extracting simulation parameters from regulatory documents.
Research Implications & Future Directions
Transforming evacuation science through actionable insights for stakeholders and comprehensive recommendations for future research.
Implications for Key Stakeholders
For Fire Safety Engineers
- • Reproducible, causally-defensible simulation inputs
- • Inclusive performance-based design tools
- • Strengthened reliability of safety cases
For Building Managers
- • Clear justification for AI guidance investment
- • Integration with real-time sensor networks
- • Enhanced vertical evacuation infrastructure
For Software Developers
- • Blueprint for next-generation simulation tools
- • Validated inclusive agent profiles
- • Robust probabilistic assessment features
Technology Integration Recommendations
🤖 Occupant Evacuation Elevators (OEEs)
Integrate AI guidance with NFPA 101-compliant OEEs for seamless vertical evacuation of individuals with disabilities.
- • Real-time capacity and status monitoring
- • Dynamic routing based on occupant mobility profiles
- • Automated dispatch coordination
📡 Real-Time Sensing Integration
Deploy multi-modal sensor networks to provide AI systems with live situational awareness.
- • LiDAR for precise occupant counting and density
- • Thermal cameras for smoke-obscured visibility
- • Wi-Fi/Bluetooth for crowd movement patterns
🏠 Smart Areas of Refuge
Transform static Areas of Refuge into intelligent, AI-managed safe zones with dynamic capacity management.
- • Real-time occupancy monitoring
- • Automated first responder notification
- • Priority-based occupant routing
🎯 Assisted Evacuation Coordination
Enable AI systems to coordinate trained personnel for optimal assisted evacuation strategies.
- • Automated triage of assistance requests
- • Optimized staff dispatch routing
- • Real-time progress tracking
Future Research Directions
🔥 Integration with High-Fidelity Hazard Models
Couple DiSFM-GS with validated CFD models like Fire Dynamics Simulator (FDS) for dynamic fire-occupant interaction studies.
📊 Expanded Empirical Data Collection
Conduct large-scale evacuation drills with diverse populations across multiple building types to improve model generalizability.
🎧 Multimodal AI Guidance Systems
Explore auditory, visual, and haptic guidance modalities using VR environments to optimize communication effectiveness.
🤝 Dynamic Trust and Social Influence Modeling
Develop agent-based trust models incorporating AI performance history and social network effects on compliance.
Ask the AI Researcher ✨
Have questions about the EvacuAIDi research? Chat with an AI assistant trained on the complete dissertation content to explore findings, methodology, and implications.
Quick questions to get started: